“Models for Environmental Literacy” by Tivon Rice
Title:
Artist(s) and People Involved:
Filmmaker, Video Artist, or Animator(s):
- Tivon Rice
-
- Delft University of Technology
Symposium:
Venue(s):
Artist Statement:
The experimental video “Models for Environmental Literacy” invites us to rethink the nature and application of artificial intelligence in the context of the environment. As three A.I. voices guide us through a series of landscapes at the intersections of nature and human intervention, we follow a dialogue somewhere within the spectrum of human and non-human language. How does our reading of this computer-generated language point back to our own personal subjectivities and our own environmental literacy? And equally so, how can encounters with non-human language act as a kind of dress rehearsal for future relationships with the Other?
In the face of climate change, large-scale computer-controlled systems are being deployed to understand terrestrial systems. Artificial intelligence is used on a planetary scale to detect, analyze, and manage landscapes. In the West, there is a great belief in ‘intelligent’ technology as a lifesaver. However, practice shows that the dominant AI systems lack the fundamental insights to act in an inclusive manner towards the complexity of ecological, social, and environmental issues. This, while the imaginative and artistic possibilities for the creation of non-human perspectives are often overlooked.
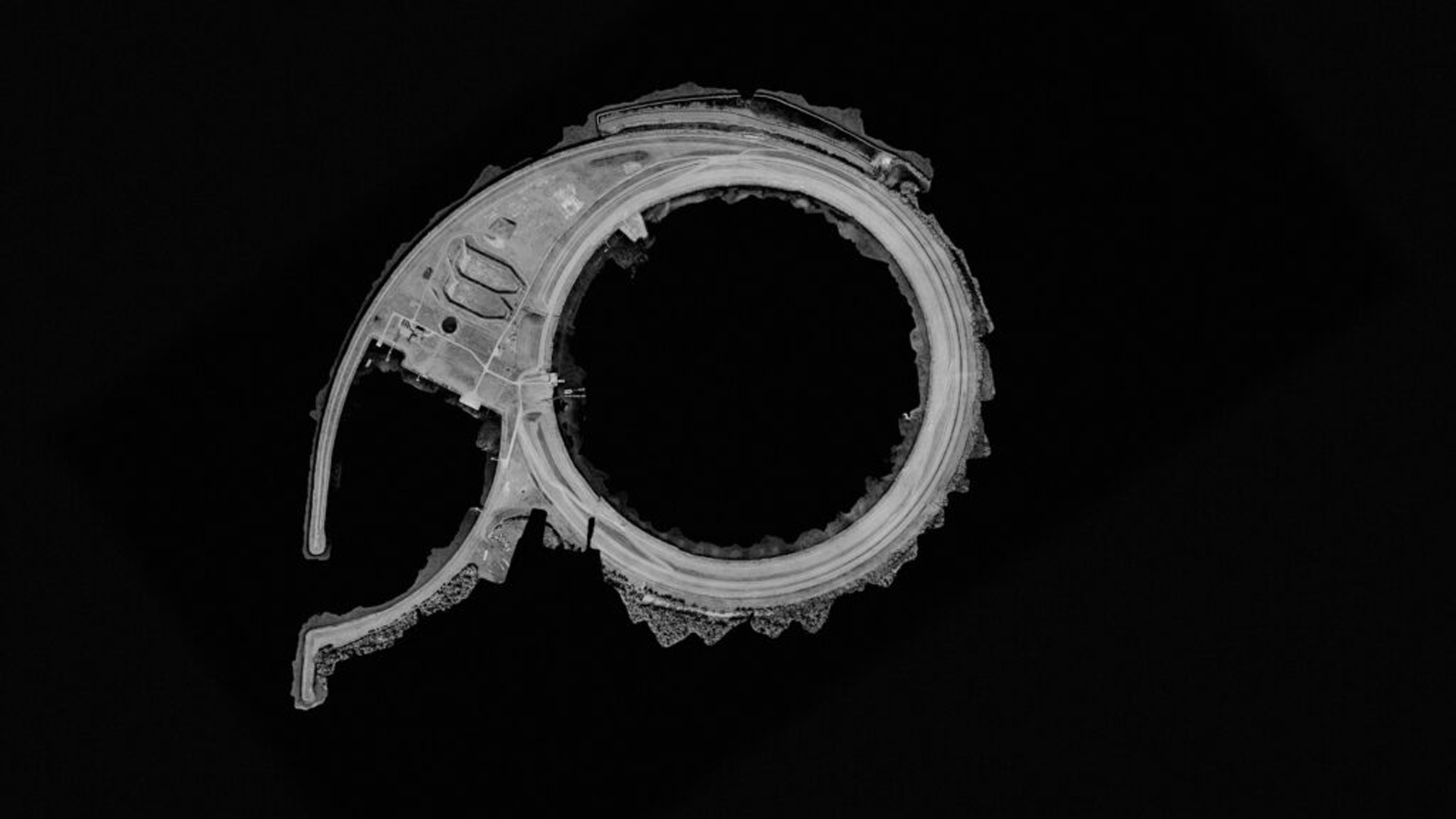
With the long-term research project and experimental films Models for Environmental Literacy, the artist Tivon Rice explores in a speculative manner how A.I.s could have alternative perceptions of an environment. Three distinct A.I.s were trained for the screenplay: the Scientist, the Philosopher, and the Author. The A.I.s each have their own personalities and are trained in literary work – from science fiction and eco-philosophy, to current intergovernmental reports on climate change. Rice brings them together for a series of conversations while they inhabit scenes from scanned natural environments. These virtual landscapes have been captured on several field trips that Rice undertook over the past two years with FIBER (Amsterdam) and BioArt Society (Helsinki).